glibc malloc/free 源码分析
代码仓库:https://github.com/bminor/glibc/blob/glibc-2.27/,只分析 64 位模式下。
关键概念
malloc_chunk
malloc 申请的内存块被称为 chunk,用 malloc_chunk 结构体表示:
/*
This struct declaration is misleading (but accurate and necessary).
It declares a "view" into memory allowing access to necessary
fields at known offsets from a given base. See explanation below.
*/
struct malloc_chunk {
INTERNAL_SIZE_T prev_size; /* Size of previous chunk (if free). */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T size; /* Size in bytes, including overhead. */
struct malloc_chunk* fd; /* double links -- used only if free. */
struct malloc_chunk* bk;
/* Only used for large blocks: pointer to next larger size. */
struct malloc_chunk* fd_nextsize; /* double links -- used only if free. */
struct malloc_chunk* bk_nextsize;
};
其中 prev_size 只有在前一个 chunk 是 free 状态的时候被使用,否则给物理相邻的前一个 chunk 当用户数据块。
至于 chunk 是什么状态,使用 chunk→size 的某些位做标记,标志位相关的宏:
/* size field is or'ed with PREV_INUSE when previous adjacent chunk in use */
#define PREV_INUSE 0x1
/* extract inuse bit of previous chunk */
#define prev_inuse(p) ((p)->mchunk_size & PREV_INUSE)
/* size field is or'ed with IS_MMAPPED if the chunk was obtained with mmap() */
#define IS_MMAPPED 0x2
/* check for mmap()'ed chunk */
#define chunk_is_mmapped(p) ((p)->mchunk_size & IS_MMAPPED)
/* size field is or'ed with NON_MAIN_ARENA if the chunk was obtained
from a non-main arena. This is only set immediately before handing
the chunk to the user, if necessary. */
#define NON_MAIN_ARENA 0x4
/* Check for chunk from main arena. */
#define chunk_main_arena(p) (((p)->mchunk_size & NON_MAIN_ARENA) == 0)
/* Mark a chunk as not being on the main arena. */
#define set_non_main_arena(p) ((p)->mchunk_size |= NON_MAIN_ARENA)
/*
Bits to mask off when extracting size
Note: IS_MMAPPED is intentionally not masked off from size field in
macros for which mmapped chunks should never be seen. This should
cause helpful core dumps to occur if it is tried by accident by
people extending or adapting this malloc.
*/
#define SIZE_BITS (PREV_INUSE | IS_MMAPPED | NON_MAIN_ARENA)
size 大小必须是 MALLOC_ALIGNMENT 的整数倍,空闲的位用作标志位:
#define MALLOC_ALIGNMENT 16
PREV_INUSE 标志位用于记录前一个 chunk 是否被分配,堆中第一个被分配的 chunk 的 PREV_INUSE 位都会被设置为 1,防止向前访问非法内存。
arena
进程的每个线程都会有个对应的存储堆信息的链表结构 heap_info:
typedef struct _heap_info
{
mstate ar_ptr; /* Arena for this heap. */
struct _heap_info *prev; /* Previous heap. */
size_t size; /* Current size in bytes. */
size_t mprotect_size; /* Size in bytes that has been mprotected
PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE. */
/* Make sure the following data is properly aligned, particularly
that sizeof (heap_info) + 2 * SIZE_SZ is a multiple of
MALLOC_ALIGNMENT. */
char pad[-6 * SIZE_SZ & MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK];
} heap_info;
每个线程的堆内存是逻辑上互相独立的,每个堆都关联一个 arena,主线程的 arena 称为 main_arena,子线程的 arena 称为 thread_arena。
arena 是一个指向 malloc_state 结构的指针:
/*
have_fastchunks indicates that there are probably some fastbin chunks.
It is set true on entering a chunk into any fastbin, and cleared early in
malloc_consolidate. The value is approximate since it may be set when there
are no fastbin chunks, or it may be clear even if there are fastbin chunks
available. Given it's sole purpose is to reduce number of redundant calls to
malloc_consolidate, it does not affect correctness. As a result we can safely
use relaxed atomic accesses.
*/
struct malloc_state
{
/* Serialize access. */
__libc_lock_define (, mutex);
/* Flags (formerly in max_fast). */
int flags;
/* Set if the fastbin chunks contain recently inserted free blocks. */
/* Note this is a bool but not all targets support atomics on booleans. */
int have_fastchunks;
/* Fastbins */
mfastbinptr fastbinsY[NFASTBINS];
/* Base of the topmost chunk -- not otherwise kept in a bin */
mchunkptr top;
/* The remainder from the most recent split of a small request */
mchunkptr last_remainder;
/* Normal bins packed as described above */
mchunkptr bins[NBINS * 2 - 2];
/* Bitmap of bins */
unsigned int binmap[BINMAPSIZE];
/* Linked list */
struct malloc_state *next;
/* Linked list for free arenas. Access to this field is serialized
by free_list_lock in arena.c. */
struct malloc_state *next_free;
/* Number of threads attached to this arena. 0 if the arena is on
the free list. Access to this field is serialized by
free_list_lock in arena.c. */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T attached_threads;
/* Memory allocated from the system in this arena. */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T system_mem;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_system_mem;
};
arena 中维护了一些关键的状态信息和链表,相关字段在用到的时候再解释。
tcache
如果启用 tcache(在 2.26 引入,默认启用),在内存分配时首先在 tcachebins 里找有没有合适的 chunk。
先对申请的内存大小按 MALLOC_ALIGNMENT **对齐,也就是 16 字节对齐,对齐方式如下:
#define MALLOC_ALIGNMENT (2 * SIZE_SZ < __alignof__ (long double) \
? __alignof__ (long double) : 2 * SIZE_SZ) // 实际就是0x10
#define MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK (MALLOC_ALIGNMENT - 1) // 0x0F
#define MIN_CHUNK_SIZE (offsetof(struct malloc_chunk, fd_nextsize)) // 0x20
#define MINSIZE \
(unsigned long)(((MIN_CHUNK_SIZE+MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK) & ~MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK)) // 0x20
// 最小分配 MINSIZE,超过后按 16 位对齐,有时候要多申请 SIZE_SZ 大小的空间(可能是要算上下一个chunk的 prev_size 位置且保证对齐)
// 例如 下面两个例子申请的大小不同,但是实际分配的 chunk 大小都是 0x20:
// 申请 0x10 的空间:
// (0x10 + 8 + 0x0f) & ~0x0f = 0x20 这时候下一个 chunk 用不到如果用到的话就不对齐了
// 申请 0x18 的空间:
// (0x18 + 8 + 0x0f) & ~0x0f = 0x20 这时候就用到了下一个 chunk 的 prev_size 了
#define request2size(req) \
(((req) + SIZE_SZ + MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK < MINSIZE) ? \
MINSIZE : \
((req) + SIZE_SZ + MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK) & ~MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK)
使用 request2size 将 bytes 参数转换为所需 chunk 的大小,chunk 头占用 0x10 的空间,剩下的用来存储用户数据。
tcache 是一种链表结构,相关的结构体 tcache_entry 和 tcache_perthread_struct:
# define TCACHE_MAX_BINS 64
typedef struct tcache_entry
{
struct tcache_entry *next;
} tcache_entry;
typedef struct tcache_perthread_struct
{
char counts[TCACHE_MAX_BINS]; // 表示每个索引下链表的长度
tcache_entry *entries[TCACHE_MAX_BINS];
} tcache_perthread_struct;
static __thread tcache_perthread_struct *tcache = NULL;
每个线程一个 tcache,每个 tcache 有 64 个 tcache_entry,每个 tcache_entry 是个单向链表结构,tcache 的每个索引存储相似大小的 chunk 链表,和其他 bin 不一样 tcache_entry 直接指向用户数据而不是 chunk 头。
不同的大小的 chunk 被划分到对应的索引里,大小和索引互相转换通过 tidx2usize 和 csize2tidx 完成:
/* 结果仅为该索引下用户数据的最大可用大小 */
# define tidx2usize(idx) (((size_t) idx) * MALLOC_ALIGNMENT + MINSIZE - SIZE_SZ)
/* 根据 chunk 大小获取索引 */
/* When "x" is from chunksize(). */
# define csize2tidx(x) (((x) - MINSIZE + MALLOC_ALIGNMENT - 1) / MALLOC_ALIGNMENT)
也就是这个关系:
idx chunk_size data_range
0 0x20 0~24
1 0x30 25~40
2 0x40 41~56
3 0x50 57~72
4 0x60 73~88
5 0x70 89~104
6 0x80 105~120
7 0x90 121~136
8 0xa0 137~152
9 0xb0 153~168
10 0xc0 169~184
11 0xd0 185~200
12 0xe0 201~216
13 0xf0 217~232
14 0x100 233~248
15 0x110 249~264
16 0x120 265~280
17 0x130 281~296
18 0x140 297~312
19 0x150 313~328
20 0x160 329~344
21 0x170 345~360
22 0x180 361~376
23 0x190 377~392
24 0x1a0 393~408
25 0x1b0 409~424
26 0x1c0 425~440
27 0x1d0 441~456
28 0x1e0 457~472
29 0x1f0 473~488
30 0x200 489~504
31 0x210 505~520
32 0x220 521~536
33 0x230 537~552
34 0x240 553~568
35 0x250 569~584
36 0x260 585~600
37 0x270 601~616
38 0x280 617~632
39 0x290 633~648
40 0x2a0 649~664
41 0x2b0 665~680
42 0x2c0 681~696
43 0x2d0 697~712
44 0x2e0 713~728
45 0x2f0 729~744
46 0x300 745~760
47 0x310 761~776
48 0x320 777~792
49 0x330 793~808
50 0x340 809~824
51 0x350 825~840
52 0x360 841~856
53 0x370 857~872
54 0x380 873~888
55 0x390 889~904
56 0x3a0 905~920
57 0x3b0 921~936
58 0x3c0 937~952
59 0x3d0 953~968
60 0x3e0 969~984
61 0x3f0 985~1000
62 0x400 1001~1016
63 0x410 1017~1032
每个索引下的单向链表最多有 7 个相同大小的 chunk:
/* This is another arbitrary limit, which tunables can change. Each
tcache bin will hold at most this number of chunks. */
# define TCACHE_FILL_COUNT 7
从 tcache bin 中存取 chunk 被包装成两个函数 tcache_put 和 tcache_get:
/* Caller must ensure that we know tc_idx is valid and there's room
for more chunks. */
static __always_inline void
tcache_put (mchunkptr chunk, size_t tc_idx)
{
tcache_entry *e = (tcache_entry *) chunk2mem (chunk);
assert (tc_idx < TCACHE_MAX_BINS);
e->next = tcache->entries[tc_idx];
tcache->entries[tc_idx] = e;
++(tcache->counts[tc_idx]);
}
/* Caller must ensure that we know tc_idx is valid and there's
available chunks to remove. */
static __always_inline void *
tcache_get (size_t tc_idx)
{
tcache_entry *e = tcache->entries[tc_idx];
assert (tc_idx < TCACHE_MAX_BINS);
assert (tcache->entries[tc_idx] > 0);
tcache->entries[tc_idx] = e->next;
--(tcache->counts[tc_idx]);
return (void *) e;
}
从这两个函数可以知道 tcachebin 中的 chunk 采用后进先出的原则进行分配。
chunk 进入 tcache 的时机:
- 内存申请
- 当在 fastbins 中找到合适的 chunk 时,将这个 chunk 所在 bin 的其他 chunk 放入 tcache
- 当在 smallbins 中找到合适的 chunk 时,将这个 chunk 所在 bin 的其他 chunk 放入 tcache
- 内存释放
- 大小符合,直接插入 tcache
被插入 tcache 的 chunk,也不会进行任何合并操作。
fastbins
如果 tcache 里没有合适的 chunk,会从 fastbins 里寻找。
fastbins 存储在 arena 的 fastbinsY 字段,是一个 malloc_chunk 链表,链表长度为 NFASTBINS:
typedef struct malloc_chunk *mfastbinptr;
#define fastbin(ar_ptr, idx) ((ar_ptr)->fastbinsY[idx])
/* offset 2 to use otherwise unindexable first 2 bins */
#define fastbin_index(sz) \
((((unsigned int) (sz)) >> (SIZE_SZ == 8 ? 4 : 3)) - 2)
/* The maximum fastbin request size we support */
#define MAX_FAST_SIZE (80 * SIZE_SZ / 4)
#define NFASTBINS (fastbin_index (request2size (MAX_FAST_SIZE)) + 1)
即 fastbins 长度为 10,使用 fastbin_index 和 csize2tidx 完成索引和 chunk 大小的相互转换,对应关系参考 tcache 的 0 - 9。
看源码好像默认只有主线程开启了 fastbins:
if (av == &main_arena)
set_max_fast (DEFAULT_MXFAST);
DEFAULT_MXFAST 只有 128 字节:
#ifndef DEFAULT_MXFAST
#define DEFAULT_MXFAST (64 * SIZE_SZ / 4)
#endif
_int_malloc 中对于是否在 fastbins 中寻找 chunk 的判断条件是:
if ((unsigned long) (nb) <= (unsigned long) (get_max_fast ()))
也就是只在 fastbins 中寻找 chunk 大小 ≤ 128 的,导致 fastbins 后面几个索引是没有用的。
另外需要注意 fastbin 只使用了 malloc_chunk 的 fd 字段组成链表,即 fastbin 链表是单向的。
bins
除了 tcache 和 fastbins 是单独存储的之外,还有 smallbins、largebins、unsortedbin,它们都在 arena 的 bins 字段存储着:
#define NBINS 128
/* Normal bins packed as described above */
mchunkptr bins[NBINS * 2 - 2];
根据 glibc 中的描述,bin0 未使用,bin1 用于 unsortedbin:
Bin 0 does not exist. Bin 1 is the unordered list; if that would be
a valid chunk size the small bins are bumped up one.
然后紧接着是 smallbins。
glibc 源码中还有一段对 bins 比较长的一段描述:
/*
Bins
An array of bin headers for free chunks. Each bin is doubly
linked. The bins are approximately proportionally (log) spaced.
There are a lot of these bins (128). This may look excessive, but
works very well in practice. Most bins hold sizes that are
unusual as malloc request sizes, but are more usual for fragments
and consolidated sets of chunks, which is what these bins hold, so
they can be found quickly. All procedures maintain the invariant
that no consolidated chunk physically borders another one, so each
chunk in a list is known to be preceeded and followed by either
inuse chunks or the ends of memory.
Chunks in bins are kept in size order, with ties going to the
approximately least recently used chunk. Ordering isn't needed
for the small bins, which all contain the same-sized chunks, but
facilitates best-fit allocation for larger chunks. These lists
are just sequential. Keeping them in order almost never requires
enough traversal to warrant using fancier ordered data
structures.
Chunks of the same size are linked with the most
recently freed at the front, and allocations are taken from the
back. This results in LRU (FIFO) allocation order, which tends
to give each chunk an equal opportunity to be consolidated with
adjacent freed chunks, resulting in larger free chunks and less
fragmentation.
To simplify use in double-linked lists, each bin header acts
as a malloc_chunk. This avoids special-casing for headers.
But to conserve space and improve locality, we allocate
only the fd/bk pointers of bins, and then use repositioning tricks
to treat these as the fields of a malloc_chunk*.
*/
大致意思是 bins 是所有释放的 chunk 的 bin 头数组,每个 bin 是双向链接的。共有 128 个 bin,有一些不是 malloc 常见的分配大小,主要是为了方便存储和寻找拆分或合并后的 chunk,并且每个 bin 链表中前后两个 chunk 不能是物理相连的内存块。
bin 中的 chunk 按大小排序,相同大小的 chunk 按 FIFO t先进先出原则存储和使用,即最近释放的 chunk 放在链表前面,分配时优先使用后面的 chunk。smallbin 中的 chunk 大小都是相同的所以不需要排序,但排序对 largebin 的分配很有用,不需要很多次遍历就能很快找到合适大小的 chunk。
为了简化这个双向链表结构,使用 repositioning tricks 技术将 malloc_chunk 重叠平铺在 bins 上作为 bin 头,实际只用到了 malloc_chunk 中的 fd 和 bk 字段:
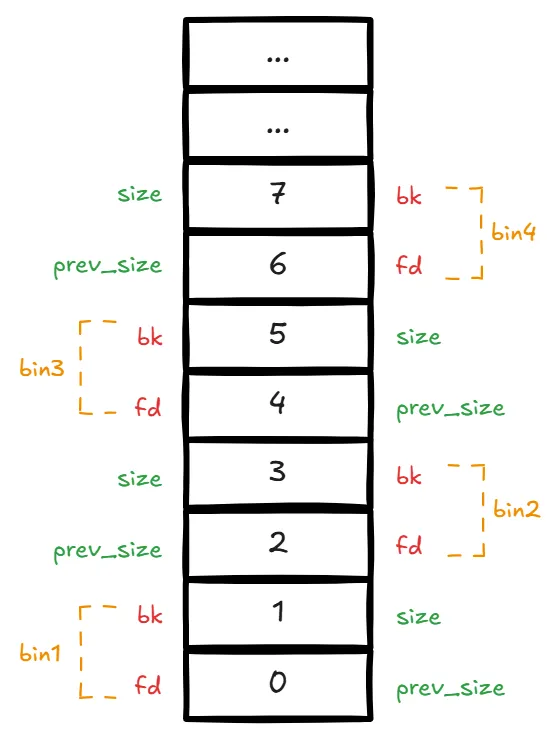
一共 128 个 bin,没有 bin0,bin1 是 unsorted bin,bin2~63 是 smallbins,bin64 开始是 largebins 范围。
bin 链表结构
所有的 bin 都是这个结构:
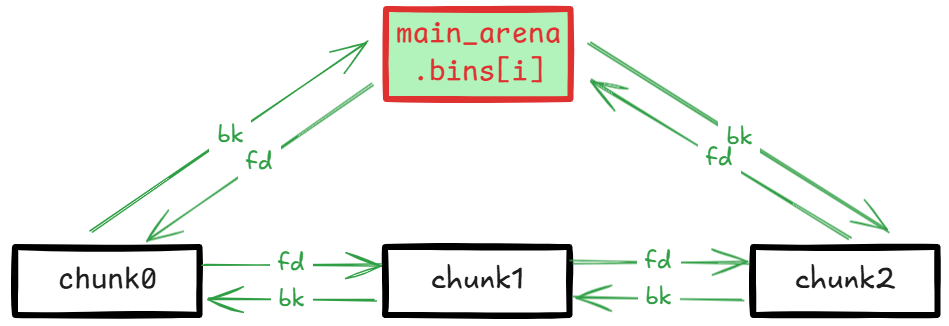
smallbins
glibc 使用 in_smallbin_range 判断 chunk 大小是否在 smallbins 范围:
#define NBINS 128
#define NSMALLBINS 64
#define SMALLBIN_WIDTH MALLOC_ALIGNMENT // 0x10
#define SMALLBIN_CORRECTION (MALLOC_ALIGNMENT > 2 * SIZE_SZ)
#define MIN_LARGE_SIZE ((NSMALLBINS - SMALLBIN_CORRECTION) * SMALLBIN_WIDTH)
#define in_smallbin_range(sz) \
((unsigned long) (sz) < (unsigned long) MIN_LARGE_SIZE)
从这些宏定义可知,smallbins 在 bins 上索引范围在 2~63,chunk 大小范围在 0x20 ~ 0x3f0 之间。
使用 smallbin_index 将 chunk 大小转换为对应的 bins 索引:
#define smallbin_index(sz) \
((SMALLBIN_WIDTH == 16 ? (((unsigned) (sz)) >> 4) : (((unsigned) (sz)) >> 3))\
+ SMALLBIN_CORRECTION)
得到 bins 索引和 smallbin chunk 大小对应关系如下:
idx chunk_size
2 0x20
3 0x30
4 0x40
5 0x50
6 0x60
7 0x70
8 0x80
9 0x90
10 0xa0
11 0xb0
12 0xc0
13 0xd0
14 0xe0
15 0xf0
16 0x100
17 0x110
18 0x120
19 0x130
20 0x140
21 0x150
22 0x160
23 0x170
24 0x180
25 0x190
26 0x1a0
27 0x1b0
28 0x1c0
29 0x1d0
30 0x1e0
31 0x1f0
32 0x200
33 0x210
34 0x220
35 0x230
36 0x240
37 0x250
38 0x260
39 0x270
40 0x280
41 0x290
42 0x2a0
43 0x2b0
44 0x2c0
45 0x2d0
46 0x2e0
47 0x2f0
48 0x300
49 0x310
50 0x320
51 0x330
52 0x340
53 0x350
54 0x360
55 0x370
56 0x380
57 0x390
58 0x3a0
59 0x3b0
60 0x3c0
61 0x3d0
62 0x3e0
63 0x3f0
largebins
从 bin64 开始都属于 largebin,每个 largebin 上的 chunk 大小不是相同的,而是一个范围。
可以先看一下 chunk 大小和 bin 索引的转换关系:
#define largebin_index_32(sz) \
(((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) <= 38) ? 56 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) <= 20) ? 91 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) <= 10) ? 110 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) <= 4) ? 119 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) <= 2) ? 124 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) :\
126)
#define largebin_index_32_big(sz) \
(((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) <= 45) ? 49 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) <= 20) ? 91 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) <= 10) ? 110 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) <= 4) ? 119 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) <= 2) ? 124 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) :\
126)
// XXX It remains to be seen whether it is good to keep the widths of
// XXX the buckets the same or whether it should be scaled by a factor
// XXX of two as well.
#define largebin_index_64(sz) \
(((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) <= 48) ? 48 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) <= 20) ? 91 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) <= 10) ? 110 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) <= 4) ? 119 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) <= 2) ? 124 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) :\
126)
#define largebin_index(sz) \
(SIZE_SZ == 8 ? largebin_index_64 (sz) \
: MALLOC_ALIGNMENT == 16 ? largebin_index_32_big (sz) \
: largebin_index_32 (sz))
64 位模式下只需要关注 largebin_index_64。smallbins 之间的大小间隔是固定的 0x10,最大的 chunk 大小是 0xf0,所以 largebin 最小 chunk 大小就是 0x400,根据 largebin_index_64 可知,largebins 按 chunk 大小不同的间隔被分成了 6 组:
| n | 数量 | 间隔(2^i) | i |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 32 | 64 | 6 |
| 2 | 16 | 512 | 9 |
| 3 | 8 | 4096 | 12 |
| 4 | 4 | 32768 | 15 |
| 5 | 2 | 262144 | 18 |
| 6 | 1 |
实际索引和 chunk 大小范围的对应关系:
64 0x400-0x430
65 0x440-0x470
66 0x480-0x4b0
67 0x4c0-0x4f0
68 0x500-0x530
69 0x540-0x570
70 0x580-0x5b0
71 0x5c0-0x5f0
72 0x600-0x630
73 0x640-0x670
74 0x680-0x6b0
75 0x6c0-0x6f0
76 0x700-0x730
77 0x740-0x770
78 0x780-0x7b0
79 0x7c0-0x7f0
80 0x800-0x830
81 0x840-0x870
82 0x880-0x8b0
83 0x8c0-0x8f0
84 0x900-0x930
85 0x940-0x970
86 0x980-0x9b0
87 0x9c0-0x9f0
88 0xa00-0xa30
89 0xa40-0xa70
90 0xa80-0xab0
91 0xac0-0xaf0
92 0xb00-0xb30
93 0xb40-0xb70
94 0xb80-0xbb0
95 0xbc0-0xbf0
96 0xc00-0xc30
97 0xc40-0xdf0
98 0xe00-0xff0
99 0x1000-0x11f0
100 0x1200-0x13f0
101 0x1400-0x15f0
102 0x1600-0x17f0
103 0x1800-0x19f0
104 0x1a00-0x1bf0
105 0x1c00-0x1df0
106 0x1e00-0x1ff0
107 0x2000-0x21f0
108 0x2200-0x23f0
109 0x2400-0x25f0
110 0x2600-0x27f0
111 0x2800-0x29f0
112 0x2a00-0x2ff0
113 0x3000-0x3ff0
114 0x4000-0x4ff0
115 0x5000-0x5ff0
116 0x6000-0x6ff0
117 0x7000-0x7ff0
118 0x8000-0x8ff0
119 0x9000-0x9ff0
120 0xa000-0xfff0
121 0x10000-0x17ff0
122 0x18000-0x1fff0
123 0x20000-0x27ff0
124 0x28000-0x3fff0
125 0x40000-0x7fff0
126 0x80000-∞
unsortedbin
对于暂时未归类到 smallbins 或 largebins 的 chunk,暂时放到 unsortedbin 里,位于 bin1 位置,不需要按大小排序。
刚释放的 chunk 不会立刻进行归类,会先放到 unsortedbin 上。
等下次调用 malloc 分配内存时,当 tcache、fastbins、smallbins 没有相同大小(exact-fit)的 chunk 时,就会对 unsortedbin 归类。
内存分配
程序调用 glibc 分配内存的入口为 __libc_malloc。
__libc_malloc
函数原型:
void *
__libc_malloc (size_t bytes)
bytes 是程序实际申请的内存大小。
如果 __malloc_hook 位置不是 null,则调用 __malloc_hook 返回。
根据所需 chunk 大小,在 tcachebins 中如果已有相同大小的 chunk,则将该 chunk 从 tcache 链表中取出后返回。
如果 tcache 中没有,则找到线程对应的 arena,调用 _int_malloc 申请内存后返回。
_int_malloc
函数原型:
static void *
_int_malloc (mstate av, size_t bytes)
av 为线程对应的 arena,bytes 为程序实际申请的内存大小。
使用 request2size 将 bytes 参数转换为所需 chunk 的大小 nb,chunk 头占用 0x10 的空间,剩下的用来存储用户数据。
如果 av 是空的,表示还没有可用的 arena,直接调用 sysmalloc 申请 mmap 映射内存并生成 chunk,此 chunk 会被标记为 IS_MMAPPED。
如果 arena 可用且 nb 大小在 fastbins 范围内,则找到合适大小的 fastbin,取出一个 chunk 后将其他相同大小的 chunk 转移到 tcache 中,达到 tcachebin 上限(7个 chunk)后停止转移。
在 fastbins 中没找到合适的,再判断 nb 是 smallbin 范围还是 largebin 范围。
如果在 smallbins 范围,找到合适大小的 smallbin ,取出一个 chunk 后将其他相同大小的 chunk 转移到 tcache 中,达到 tcachebin 上限(7个 chunk)后停止转移。
如果在 largebins 范围则调用 malloc_consolidate 合并 fastbins 中的 chunk 避免免空间碎片化。
遍历 unsorted chunk,如果 nb 在 smallbins 范围且 unsortedbin 只有一个 chunk,chunk 大小比 nb 大,并且这个 chunk 是最后一次拆分 small chunk 剩余的 chunk(由 arena 的 last_remainder 字段记录),则从这个剩余 chunk 中继续划分出一块:
/*
If a small request, try to use last remainder if it is the
only chunk in unsorted bin. This helps promote locality for
runs of consecutive small requests. This is the only
exception to best-fit, and applies only when there is
no exact fit for a small chunk.
*/
if (in_smallbin_range (nb) &&
bck == unsorted_chunks (av) &&
victim == av->last_remainder &&
(unsigned long) (size) > (unsigned long) (nb + MINSIZE))
{
否则继续遍历 unsorted chunk,对所有 unsorted chunk 进行整理,即将 unsorted chunk 转移到 smallbin、largebin 中,转移到 largebin 时需要按大小顺序排列将 chunk 插入到对应位置。
遍历过程中如果遇到 chunk 大小正好是 nb ,且符合 tcache 要求 tcache chunk 且没达上限就先存入 tcahce 并标记然后继续遍历下一个 unsorted chunk,如果无法存入 tcache 则将 chunk 直接返回给程序,结束 unsorted chunk 遍历。
在 unsorted chunk 完成转移之后,如果到达了 tcache 处理上限且之前已经有合适的 chunk 被放入 tcache,则从 tcache 获取 chunk 返回给程序。默认无上限,即不会走这一步。
如果遍历次数到达 10000 次终止遍历。
如果之前找到了 chunk 并存入了 tcache,则从 tcache 获取 chunk 返回给程序。
如果nb 在 largebins 范围,则找到满足 nb 的最小的 large chunk 进行拆分操作,并将拆分后剩余的 chunk 放入 unsortedbin 并记录到 arena 的 last_remainder 字段,将 chunk 返回给程序。
如果还是没有合适的,则从所有 bins 中找到满足 nb 的最小 chunk,如果有多个相同大小的 chunk,则按最近最少使用的原则选取 chunk 进行拆分操作,并将拆分后剩余的 chunk 放入 unsortedbin 并记录到 arena 的 last_remainder 字段,将 chunk 返回给程序。
如果在 bins 中都没有满足需求的 chunk,就从 top chunk 中划分出一块,top chunk 不够的话调用 sysmalloc 对 top 扩容并分配 chunk 返回给程序。
malloc_consolidate
函数原型:
static void malloc_consolidate(mstate av)
该函数遍历所有 fastbin 中的 chunk。
如果 chunk 的 PREV_INUSE 标记位不是 1,说明物理相连的前一个 chunk 是空闲状态,就将当前 chunk 向前合并,再判断物理相连的后一个 chunk 是否是空闲,如果也是空闲就再合并,最后得到一个新的 chunk,新 chunk 的 PREV_INSUE 标志位置为 1。
如果合并后的新 chunk 和 top chunk 物理相连了,则直接设置为 top chunk。否则链到 unsortedbin 上。
在合并过程上涉及将 chunk 从 bin 链表上移除,这个操作通过 unlink 函数完成,因为是一个常用操作,所以被定义为一个宏:
/* Take a chunk off a bin list */
#define unlink(AV, P, BK, FD) { \
if (__builtin_expect (chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P)), 0)) \
malloc_printerr ("corrupted size vs. prev_size"); \
FD = P->fd; \
BK = P->bk; \
if (__builtin_expect (FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P, 0)) \
malloc_printerr ("corrupted double-linked list"); \
else { \
FD->bk = BK; \
BK->fd = FD; \
if (!in_smallbin_range (chunksize_nomask (P)) \
&& __builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize != NULL, 0)) { \
if (__builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize != P, 0) \
|| __builtin_expect (P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != P, 0)) \
malloc_printerr ("corrupted double-linked list (not small)"); \
if (FD->fd_nextsize == NULL) { \
if (P->fd_nextsize == P) \
FD->fd_nextsize = FD->bk_nextsize = FD; \
else { \
FD->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; \
FD->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; \
P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = FD; \
P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = FD; \
} \
} else { \
P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; \
P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; \
} \
} \
} \
}
sysmalloc
函数原型:
static void *
sysmalloc (INTERNAL_SIZE_T nb, mstate av)
nb 参数表示所需 chunk 的大小,av 是线程对应的 arena。
当满足以下三个任一条件时,直接调用 mmap 申请映射内存 chunk 并被标记为 IS_MMAPPED,而不是扩展已有堆内存:
av是空,表示没有可用的 arenanb超过了阈值 DEFAULT_MMAP_THRESHOLD,默认是 128 * 1024 = 0x20000- 当前申请的 mmap 内存数量没有超过 DEFAULT_MMAP_MAX,默认是 65536
mmap 内存申请暂不做具体分析,先跳过。
如果即没有可用的 arena 也没有申请到 mmap 内存,则直接返回空。
如果 av 不为空,则表示有可用的 arena,通过扩展 av->top 后从 av->top 中划分出所需 chunk 块。
线程申请的内存 chunk 时实际是从 arena 中的 top chunk 中划分出来的,sysmalloc 函数用于扩展 topchunk 后分配 chunk。
如果topchunk对于申请的大小还有足够的空间,则直接触发异常:
/* Precondition: not enough current space to satisfy nb request */
assert ((unsigned long) (old_size) < (unsigned long) (nb + MINSIZE));
如果 av 是 thread_arena,首先尝试调用 grow_heap 扩展 top 堆,如果失败就调用 new_heap 创建新堆。
new_heap 中实际是利用 mmap 方式分配内存。new_heap 中限制一个 mmap 堆的最大空间默认是 HEAP_MAX_SIZE,分配的最小堆大小为 HEAP_MIN_SIZE:
#define HEAP_MIN_SIZE (32 * 1024)
#ifndef HEAP_MAX_SIZE
# ifdef DEFAULT_MMAP_THRESHOLD_MAX
# define HEAP_MAX_SIZE (2 * DEFAULT_MMAP_THRESHOLD_MAX)
# else
# define HEAP_MAX_SIZE (1024 * 1024) /* must be a power of two */
# endif
#endif
如果超过这个限制就会分配失败,sysmalloc 再尝试直接调用 mmap 创建所需大小的映射内存块。
如果 av 是 main_arena,则利用 brk 方式分配内存,如果 brk 失败则调用 mmap 分配内存。因为这种 brk 和 mmap 混合使用的情况所以可能会造成内存无法连续,具体 brk 分配过程不再细做分析,先跳过。
不管是 main_arena 还是 thread_arena,因为 top_pad 的存在:
{ /* Request enough space for nb + pad + overhead */
size = nb + mp_.top_pad + MINSIZE;
nb 是请求 chunk 块的大小,最小 0x20,mp_.top_pad 默认是 DEFAULT_TOP_PAD,即 0x20000:
#ifndef DEFAULT_TOP_PAD
# define DEFAULT_TOP_PAD 131072
#endif
所以 top 堆的最小长度为 0x20040,没有最大限制。另外 top 堆长度还要与系统 page_size 对齐。
最终 top 堆完成扩容操作。然后从 top 堆顶划分出 nb 长度的 chunk 块返回。
内存释放
程序调用 glibc 释放内存的入口为 __libc_free。
__libc_free
函数原型:
void
__libc_free (void *mem)
mem 是要释放的内存位置。
如果 __free_hook 位置不是 null,则调用 __free_hook 返回。
调用 mem2chunk 将 mem 转为 chunk。
如果 chunk 的 IS_MMAPPED 标记位为 1,表示为 map 申请的大内存或临时内存,需要立即释放。
否则调用 _int_free 释放内存。
_int_free
函数原型:
static void
_int_free (mstate av, mchunkptr p, int have_lock)
如果 chunk 满足存入 tcache 的条件,则将 chunk 存入 tcache 中,完成释放。
如果 chunk 满足存入 fastbins 的条件,则将 chunk 存入 fastbins 中。
如果不能存入 fastbins,将 IS_MMAPPED 标记位为 1 的 chunk 释放归还给系统,否则对 chunk 物理连续的前后空闲 chunk 进行合并。
如果合并后的 chunk 没有到 top chunk 边界,就将 chunk 放入 unsorted bin 中,否则说明 top chunk 耗尽了直接该释放的 chunk 作为 top chunk。
最后对于经过合并操作后的 chunk 大小如果超过了 FASTBIN_CONSOLIDATION_THRESHOLD 阈值,则调用 malloc_consolidate 合并 fastbin chunk:
/*
FASTBIN_CONSOLIDATION_THRESHOLD is the size of a chunk in free()
that triggers automatic consolidation of possibly-surrounding
fastbin chunks. This is a heuristic, so the exact value should not
matter too much. It is defined at half the default trim threshold as a
compromise heuristic to only attempt consolidation if it is likely
to lead to trimming. However, it is not dynamically tunable, since
consolidation reduces fragmentation surrounding large chunks even
if trimming is not used.
*/
#define FASTBIN_CONSOLIDATION_THRESHOLD (65536UL)
/*
If freeing a large space, consolidate possibly-surrounding
chunks. Then, if the total unused topmost memory exceeds trim
threshold, ask malloc_trim to reduce top.
Unless max_fast is 0, we don't know if there are fastbins
bordering top, so we cannot tell for sure whether threshold
has been reached unless fastbins are consolidated. But we
don't want to consolidate on each free. As a compromise,
consolidation is performed if FASTBIN_CONSOLIDATION_THRESHOLD
is reached.
*/
if ((unsigned long)(size) >= FASTBIN_CONSOLIDATION_THRESHOLD) {
if (atomic_load_relaxed (&av->have_fastchunks))
malloc_consolidate(av);
总结
释放:将 mmap 临时内存 chunk 直接释放,其他 chunk 不会被立即释放,按 tcache(64) > fastbins(10) > unsortedbin(1) 的优先级存入作为空闲 chunk,进入到 unsortedbin 之前要先进行合并操作。
分配:如果没有 arena 直接分配 mmap 临时内存 chunk,否则按 tcache(64) > fastbins(10) > smallbins(62) > unsortedbin(1) > largebins > topchunk 的优先级寻找合适大小的空闲 chunk,优先寻找相同大小的 chunk,如果没有大小正合适(exact-fit)的 chunk 就从大小最接近的 chunk 上分隔出一块,topchunk 负责兜底,topchunk 也没办法就做系统调用扩展 topchunk 后再划分一块给程序。
几个重要点:
- tcache、fastbin 都是单向链表,其他 bin 都是双向。
- 程序连续申请内存分配,由于 topchunk 的存在,很大概率是连续的内存段
- 几次申请到的内存段如果连续,发生堆溢出时会影响之后与其连续内存的 chunk 头形成畸形,导致 free chunk 和使用中 chunk 发生重叠或 free chunk 被链接到任意位置
- 程序连续释放和分配相同大小的内存,背后实际都是同一段内存,如果程序存在 UAF 漏洞可导致 free 状态的 chunk 被链接到任意位置
- 如果 free chunk 能被链接到任意位置,就可以实现在任意位置上分配内存,从而达到任意位置读写的目的